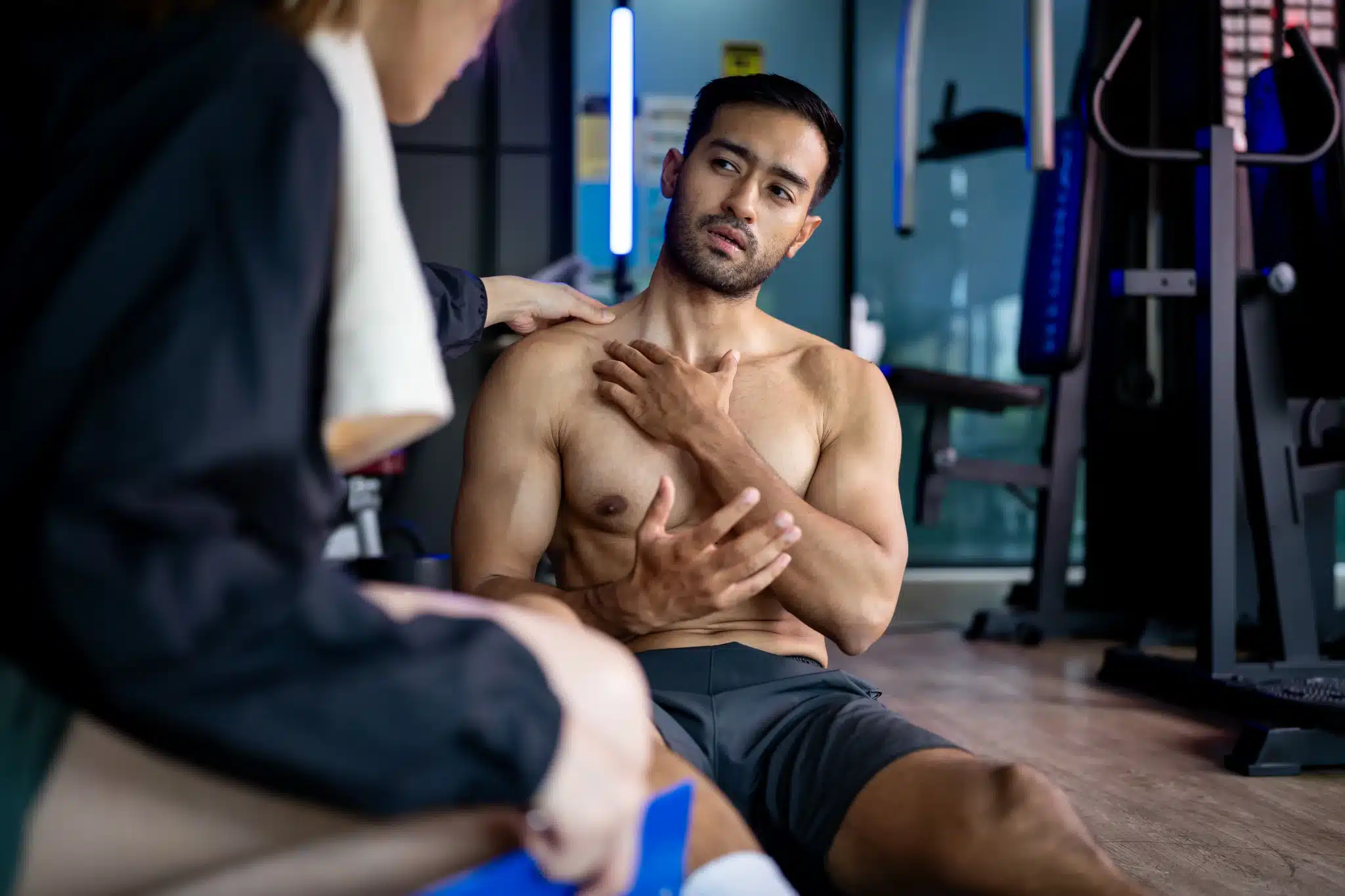
Is that constant ache in your lower back just from a bad night's sleep or too much work? Lumbosacral back pain is a common problem worldwide. It's not something to ignore, especially if you feel stiff, have sharp pain, or can't move as well as you used to. But what causes it, and how can you make it better?
This pain can come from many sources, like muscle or tendon injuries, arthritis, or disc problems. It can make everyday tasks hard and lower your quality of life. Knowing the m54.59 diagnosis code and understanding the m54 59 other low back pain category is key. This pain starts in the lumbar area and can range from a sharp, short pain to a long-lasting, severe condition. Since low back pain is a big reason for missed work in the U.S., it's important to tackle it quickly.
A detailed anatomical illustration of the human lower back, highlighting the lumbosacral region with labels for key components like vertebrae, discs, and muscles. The image should show areas of tension and inflammation, depicted in warm colors to indicate pain. Include a subtle background of a gradient transitioning from cool to warm tones, symbolizing discomfort and healing.
Key Takeaways
- Chronic lower back pain frequently disrupts daily activities and job performance.
- Proper diagnosis, including the use of m54.59 diagnosis code, is vital for effective treatment.
- Both muscle/tendon injuries and degenerative conditions like arthritis can lead to lumbosacral back pain.
- Addressing pain early with physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments can prevent it from becoming chronic.
- Low back pain affects almost everyone at some point in their lives, often manifesting initially in their 30s.
- Acupuncture, massages, and yoga have shown varied success in alleviating chronic back pain.
Causes of Lumbosacral Back Pain
Lumbosacral back pain is common and can affect anyone. It doesn't matter if you've had an injury or not. Knowing what causes it can help find the right treatment.
Muscle Strain and Overuse
Lower back pain often comes from lifting heavy objects or doing too much exercise. This overworks the muscles, leading to pain. It's key to lift correctly to avoid injury.
Arthritis and Degenerative Conditions
Arthritis of the spine is another big reason for back pain. It happens as we get older and our spine wears out. Dr. Akhil Chhatre from Johns Hopkins says this is a major cause of back pain in older people.
Herniated Discs and Sciatica
A herniated disc happens when the soft part of the disc bulges out. This puts pressure on nerves, causing pain in the legs, known as sciatica. It's important to manage this condition to avoid nerve damage.
Lifestyle Factors
Our lifestyle choices can also lead to back pain. Smoking, being overweight, and sitting too much increase the risk. How we lift and our posture can also strain our backs. Staying active and lifting right can help prevent this.

A detailed anatomical illustration depicting the human spine with a focus on the lumbosacral area, highlighting various causes of back pain such as muscle strain, herniated discs, sciatica, and degenerative diseases. Include visual representations of poor posture, lifting heavy objects, and physical activity impacts, all set against a neutral background for clarity.
| Factor | Impact on Lumbosacral Back Pain |
|---|---|
| Muscle Strain | Causes overuse and inflammation |
| Arthritis of the Spine | Leads to chronic pain and stiffness |
| Herniated Disc | Results in nerve compression and sciatica |
| Lifestyle Factors | Contributes through unhealthy habits like smoking and poor posture |
It's vital to know these causes and get help for ongoing back pain. Services like chirotouch billing can make getting treatment easier and faster.
Common Symptoms of Lumbosacral Back Pain
Lumbosacral back pain is a common issue worldwide. A 2020 study found it's the top reason for missing work and the most disabling condition.
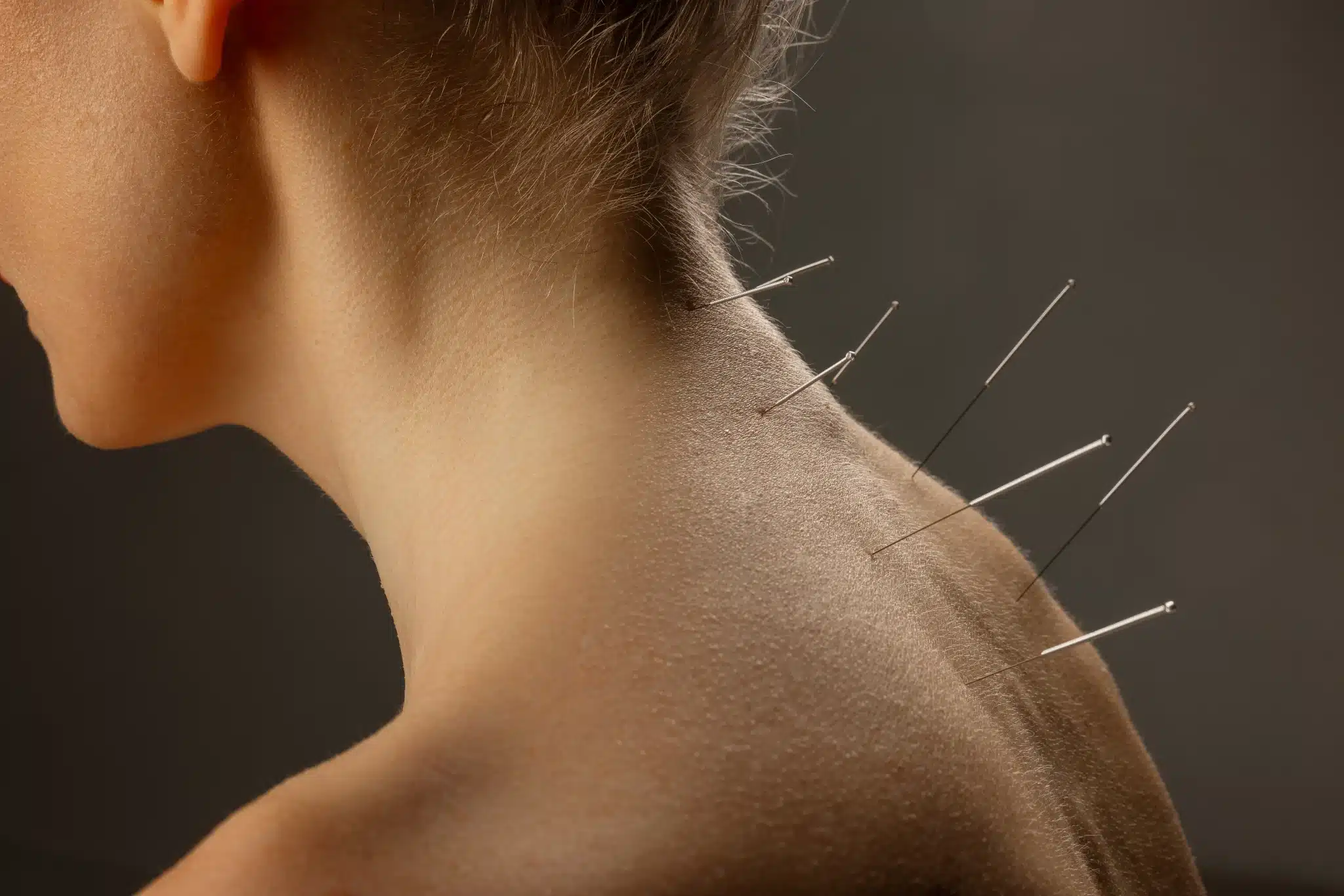
A serene acupuncture clinic with a focus on lumbosacral back pain, featuring a patient lying calmly on an acupuncture table surrounded by soothing colors, natural light filtering through large windows, soft pillows for comfort, acupuncture needles delicately placed along the lower back, and calming decor elements like plants and artwork that evoke relaxation and healing.
Pain Characteristics
The pain from lumbosacral back pain can feel like a dull ache or sharp stabbing. It can make it hard to move or stand up straight. Most people first experience back pain between 30 and 50 years old.
Acute back pain lasts a few days to weeks. Chronic back pain lasts over three months. For long-term pain, acupuncture is helpful. It targets specific acupuncture points for chronic lower back pain, offering a different treatment option.
Associated Symptoms
Other symptoms include leg weakness, fever, or pain that gets worse when coughing or sneezing. These symptoms need quick medical attention.
Smoking, obesity, and poor posture can make back pain worse. Leg weakness and fever with back pain are especially concerning. They require a doctor's visit. Effective treatments include physical therapy, medications, and acupuncture.
To tackle lumbosacral back pain, we need a full plan. This includes treatments and ways to prevent it. Using modern methods like acupuncture for chronic lower back pain helps many. It shows the value of holistic treatments for this common problem.
Diagnosing Lumbosacral Back Pain
Diagnosing lumbosacral back pain needs a detailed approach. This helps understand the symptoms and their causes. Low back pain affects up to 84 percent of adults at some point.
Clinical Examination
The first step is a clinical examination for back pain. Doctors talk about the pain type, when it started, and any other symptoms. They might find mechanical issues like muscle strain or herniated discs.
These issues are common in 97% of low back pain cases. The m54.59 icd 10 code is often used to record these diagnoses.
Doctors also look at a patient's history. They check for regular activities or incidents that caused the pain. Two out of three adults will experience low back pain at some time.
Quick medical help is advised if back pain comes with fever, numbness, or trouble urinating.
Imaging and Diagnostic Tests
Imaging is used for more serious or ongoing cases. Conditions like spinal stenosis or osteoporosis might need imaging. But, MRI, X-ray, or CT scans are usually not needed unless treatments fail.
The m54.59 icd 10 code helps decide on imaging if symptoms last beyond the initial phase.
Here is a comparative table summarizing the diagnostic approach:
| Diagnostic Tool | Purpose | Common Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Examination | Assess pain characteristics and history | Acute, low back pain, muscle strain, initial evaluation |
| MRI | Detailed imaging for persistent symptoms | Suspected herniated discs, spinal stenosis |
| X-ray | Bony abnormalities and injury | Trauma, osteoarthritis |
| CT Scan | Cross-sectional imaging | Complex or unclear cases |
Understanding the diagnostic process for lumbosacral back pain is key. It helps plan effective treatments. Most back pain comes from mechanical issues, so quick action and prevention can help a lot.
Effective Treatment Options
Dealing with lumbosacral back pain requires a mix of strategies. These are based on the person's condition and lifestyle. Here are some main treatment options:
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy is key in treating lumbosacral back pain. It includes exercises that strengthen back and abdominal muscles. This helps maintain good posture and lowers the chance of pain coming back.
Activities like meditation, yoga, and tai chi also play a role. They help with the mental side of chronic back pain. They promote relaxation and reduce muscle tension.
Medication and Pain Management
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen are often used. They help reduce inflammation and provide relief. For persistent pain, stronger treatments might be needed if home treatments don't work after a few weeks.
However, opioids are not usually the first choice. This is because they can lead to addiction and tolerance.
Acupuncture and Alternative Therapies
Alternative treatments, especially acupuncture for chronic back pain, are recognized for their effectiveness. Acupuncture works by stimulating specific body points to ease pain. It's also used for issues like smoking and weight loss.
Massage therapy and other holistic methods also help manage pain and improve well-being.
Surgical Interventions
If other treatments don't work, surgery might be considered. Procedures like spinal fusion or discectomy can help with severe conditions. Electromyography (EMG) can show if nerve pressure is present, helping decide if surgery is needed.
While surgery is a last resort, it can greatly improve life for those with severe chronic back pain.
| Treatment Option | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy and Exercise | Strengthens muscles, improves posture, reduces pain recurrence |
| NSAIDs | Alleviates inflammation and pain |
| Acupuncture | Relieves chronic back pain, addresses smoking and weight loss |
| Surgical Interventions | Alleviates severe conditions, improves function |
Prevention and Lifestyle Adjustments
To lower the risk of lumbosacral back pain, adopting healthy habits is key. Keeping a healthy weight through exercise is crucial. It strengthens back muscles, which supports the spine and reduces pain.
Proper lifting techniques are vital. Avoid lifting heavy objects often. If you must lift, use your legs, not your back. Using wheeled briefcases instead of carrying heavy loads can also help.
Creating an ergonomic workstation is important to avoid sitting strain. Make sure your chair supports your lower back. Your desk should be at the right height to prevent slouching. Standing up and stretching every 10 minutes can also help.
Eating well is another important aspect. Eating a balanced diet rich in vegetables helps manage weight. Avoiding too much red meat and simple carbs can also reduce back stress. Healthy fats from wild salmon, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and avocado are good for overall health.
Being active is key for healthy weight management and pain reduction. Even small increases in daily activity can lead to big health benefits.
Cognitive behavioral therapy and meditation help manage stress. Stress hormones can make muscles tense and increase pain. So, relaxation techniques are crucial for back pain sufferers.
Not getting enough sleep can make pain worse. Good sleep hygiene, like a consistent routine and avoiding blue light before bed, is important. Starting with meditation before sleep can also improve sleep quality and reduce pain.
Acupuncture can help with chronic pain and improve physical function. It has been used for thousands of years in China for pain relief and rehabilitation.
About 31 million Americans have lower back pain at any time. Staying close to your ideal weight can help control it. Also, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol as they increase inflammation and pain.
Setting realistic weight goals and adopting a balanced lifestyle, like using an ergonomic workstation, are key to preventing lumbar back pain.
Conclusion
Lumbosacral back pain can be managed with the right strategies. A good plan includes early diagnosis, tailored treatments, and prevention. This can greatly reduce pain and enhance life quality.
Seeking professional help early is key if pain persists. Try different treatments, from simple care to surgery if needed. Making lifestyle changes, like exercising and managing weight, also helps prevent back pain.
About 80% of people will face disabling low back pain at some point. Women make up 47% of those with chronic low back pain, while men make up 53%. Research shows weak but significant links between certain angles and sex, but not with pain or age.
Acute low back pain affects 80% of people, and 90% of cases get better in 6 weeks. But, many people experience back pain again, with 60-80% facing it within two years. Half of those with radiating pain get better in 6 weeks, but those who don't recover by three months have a slim chance of getting better.
| Category | Statistics |
|---|---|
| Prevalence of Low Back Pain | 80% of the population experiences it at least once |
| Recovery within 6 Weeks | 90% of acute episodes resolve |
| Recurrence Rate | 60-80% within two years |
| Initial Care Sources | 40% primary care, 40% chiropractor, 20% subspecialist |
| Economic Impact | $40 billion direct and $100+ billion indirect costs annually |
For chronic low back pain, a comprehensive approach is vital. Understanding the need for a multi-faceted treatment plan is crucial. This includes both medical and lifestyle changes. It helps manage symptoms and improves life quality.
Contact Information for Holistic Billing Services
Need help with billing for back pain treatments? Holistic Billing Services is here for you. They are located at 1402 Edgewater Dr #101, Orlando, FL 32804, United States. They specialize in chiropractic and acupuncture billing support.
Reach out to their experienced team at +1 800-741-3655. They aim to make billing easy, so you can focus on getting better. With 30% of medical claims rejected, their help is vital for a smooth healthcare process.
Back pain affects 8 out of 10 people, and many turn to chiropractic and acupuncture for relief. With Medicare now covering these treatments, accurate billing is key. Contact Holistic Billing Services today for top-notch billing support.
FAQ
What is lumbosacral back pain?
Lumbosacral back pain affects the lower back. It can come from muscle or tendon injuries, arthritis, or disc problems. This pain, stiffness, and limited movement can really get in the way of daily life.
What are the principal causes of lumbosacral back pain?
Main causes include muscle strain from lifting or exercise, overuse, and spine arthritis. Disc problems also play a role. Lifestyle factors like poor lifting, obesity, and smoking increase the risk.
What are some common symptoms of lumbosacral back pain?
Symptoms range from dull aches to sharp pains. You might also feel leg weakness, pain when coughing, or fever. If these symptoms last, you should see a doctor.
How is lumbosacral back pain diagnosed?
Doctors examine the pain type, onset, and symptoms. They might use X-rays, CT scans, or MRI if treatments don't work. This is to find out if there's a more serious issue.
What are the effective treatment options for lumbosacral back pain?
Treatments include physical therapy and exercise to strengthen muscles. Medication and acupuncture are also used. For chronic pain, acupuncture can help. Surgery might be needed for severe cases.
How can lumbosacral back pain be prevented?
Prevention involves a healthy lifestyle. This includes regular exercise, managing weight, and proper lifting. An ergonomic workspace and avoiding heavy loads also help prevent back pain.
What is the m54.59 diagnosis code?
The m54.59 code is for low back pain, including lumbosacral back pain. It helps in documenting and treating lower back pain conditions.
Can acupuncture help with chronic back pain?
Yes, acupuncture can help with chronic back pain. It targets specific points to reduce pain and improve mobility. It's also good for weight loss and quitting smoking.
Where can I get assistance with chirotouch billing for back pain treatments?
Holistic Billing Services at 1402 Edgewater Dr #101, Orlando, FL 32804, specializes in chiropractic and acupuncture billing. They offer expert support and consultation at +1 800-741-3655 to help with billing, so patients can focus on treatment and recovery.
Treating M5459 Other Low Back Pain: Expert Guide
Source Links
- A Visual Guide to Low Back Pain
- Low Back Pain
- Understanding Lumbosacral Strain
- Lower Back Pain: What Could It Be?
- Back pain - Symptoms and causes
- What You Should Know About Lower Back Pain
Want to know more? Check out our related articles
Acupuncture Points for Chronic Lower Back Pain
Chronic Back Pain Acupuncture: Natural Relief Option
M54.59 Diagnosis Code: Understanding Back Pain
M54.59 ICD 10 Code: Understanding Radiculopathy